What is Thalassemia
09 Jan 2023 10:45:29
What is Thalassemia ?
- Thalassemia is a genetic disorder characterized by production of abnormal hemoglobin, and premature destruction of red blood cells resulting into Anemia.
- Thalassemia is transmitted from parents to their children. It is a genetic disease.
- The parents are carriers of disease. Carrier usually does not have disease symptoms clinically, but he or she carries the genes of the disorder.
- When both parents are CARRIERS, there are high chances of disease being passed to the next generation.
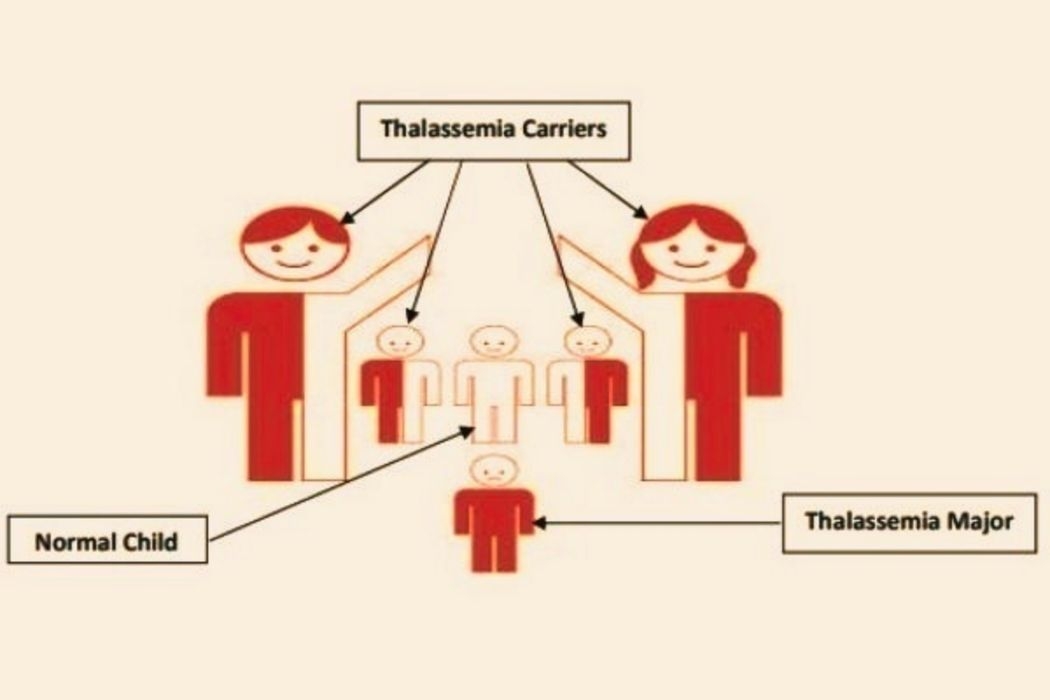
- As above figure shows, if both the parents are thalassemia carriers or minors, then there are 75 % chances for thalessamia to be transferred in the next generation and 25 % chances for the child to be a thalessamia major who will need lifelong blood transfusions. (If only one spouse is thalessamia carrier and another is normal than they can live their normal life without any trouble.)
- In thallasemia major, patient requires monthly blood transfusion FOR THE WHOLE LIFE. The patient in addition suffers from complications due to disease itself and due to blood transfusions.
- Kids who receive frequent blood transfusions may have to take medications to remove excess iron from their body-Chelation Therapy.
- Along with this the supportive treatment like, Treatment of infections, Vaccinations, Spleen removal if required and treatment of complications as required is also needed.
Thalessemia Carrier Rate in India –
- Southern India -1 to 3%
- Northern India-3 to 15% Carrier rate especially high in-
- Sindhis Punjabis Bhanushalis (North India)
- Kutchis, Lohana’s (Gujarat)
- Mahar, Neobuddhist’s, Koli’s, Agri’s, Muslims (Maharashtra)
- Gowda’s and Lingayat’s (Karnataka)
Higher rates are related to consanguineous marriage . i. e. marriages amongst relatives
What Parents of thalessamic child has to suffer ?
Tremendous psychological stress
Agony to see many needle pricks of child
Frequent hospitalization
Complications of disease
Complications of blood transfusion
Limitations of treatment
Poor Quality of life
Limited life span of child
Treatment Expenditure
Tragedy –
- A 15-year-old thalessamic child has received around 250 units of packed red cells and 4000 injections of desferioxamine.
- He has had a needle in his body for over 40,000 hours of his life. His family has already spent Rs. 16,20,000 for chelation alone.
Diagnosis –
In most cases, thalassemia is diagnosed before a child's second birthday. Diagnosis is done by-
- Blood tests like detailed hemogram
- Hb Electrophoresis
- Sr.Feritin
- Genetic typing
Curative Treatment - Bone marrow Transplant -
- At present, thallasemia can only be cured by a procedure called a bone marrow transplant. Bone marrow, which is found inside bones, produces blood cells. In a bone marrow transplant, children are first given high doses of radiation or drugs to destroy the defective bone marrow. The bone marrow is then replaced with cells from a compatible donor, usually a healthy sibling or other relative.
- It requires set up and is Very costly, costs around 6 to 10 lakhs in private set up.
At the moment, the only practical solution for survival of children with thalassemia major is multiple and frequent blood transfusion throughout life.